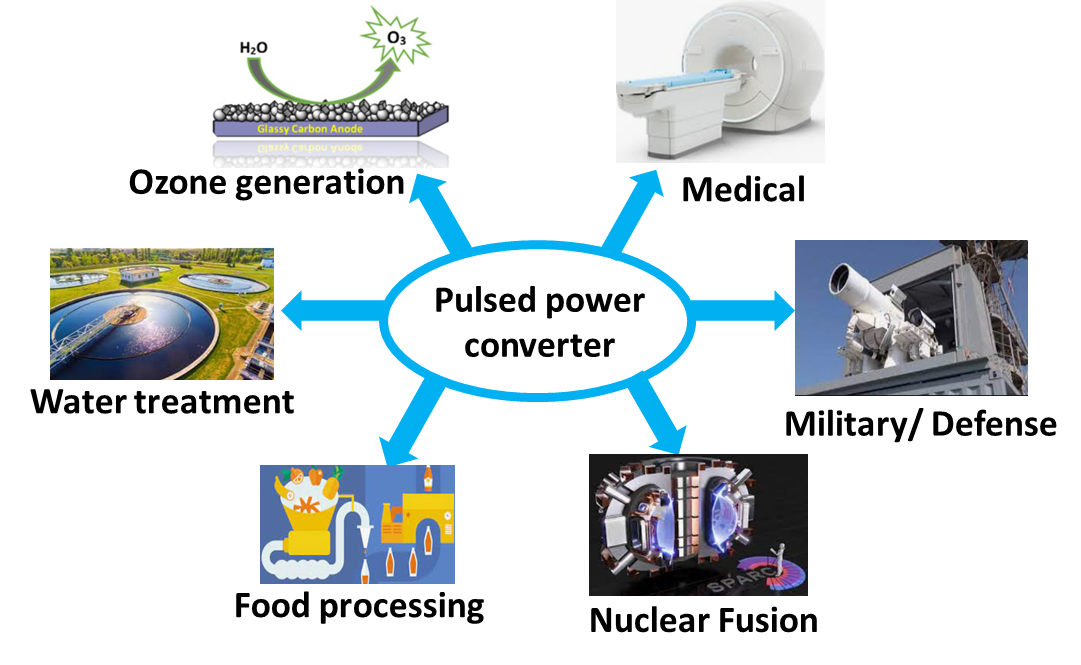
Research
Pulsed Power
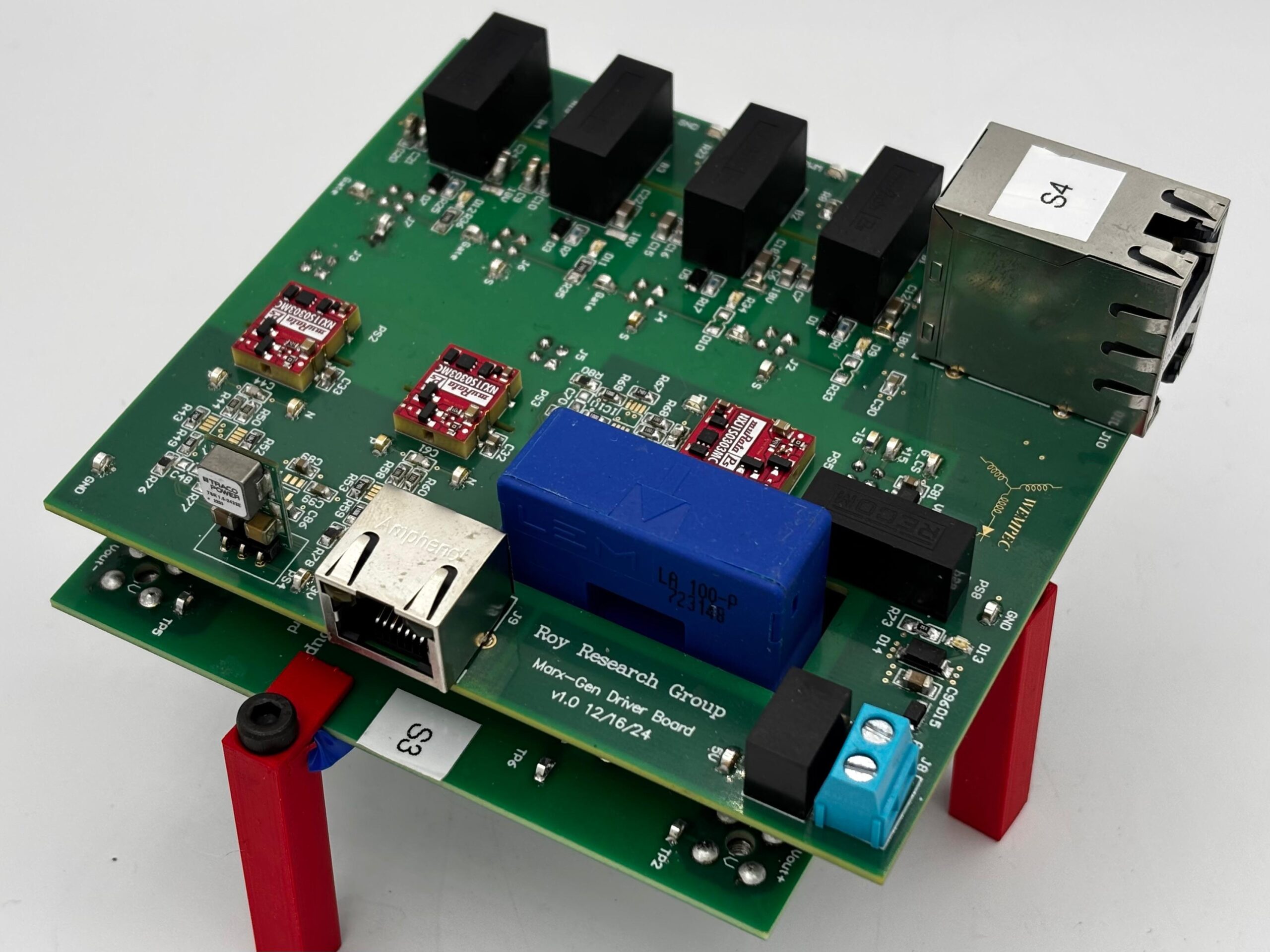
Marx Generators:
Our group leads the frontier in Solid-State Marx Generators (SSMG) and direct-switch pulsed power systems, delivering breakthrough performance where legacy designs fail:
- Ultra-fast rise times with precise flat-top control
- Inrush current mitigation & perfect stage voltage balancing
- Minimal capacitance for compact, high-power-density systems
- Arbitrary pulse shaping
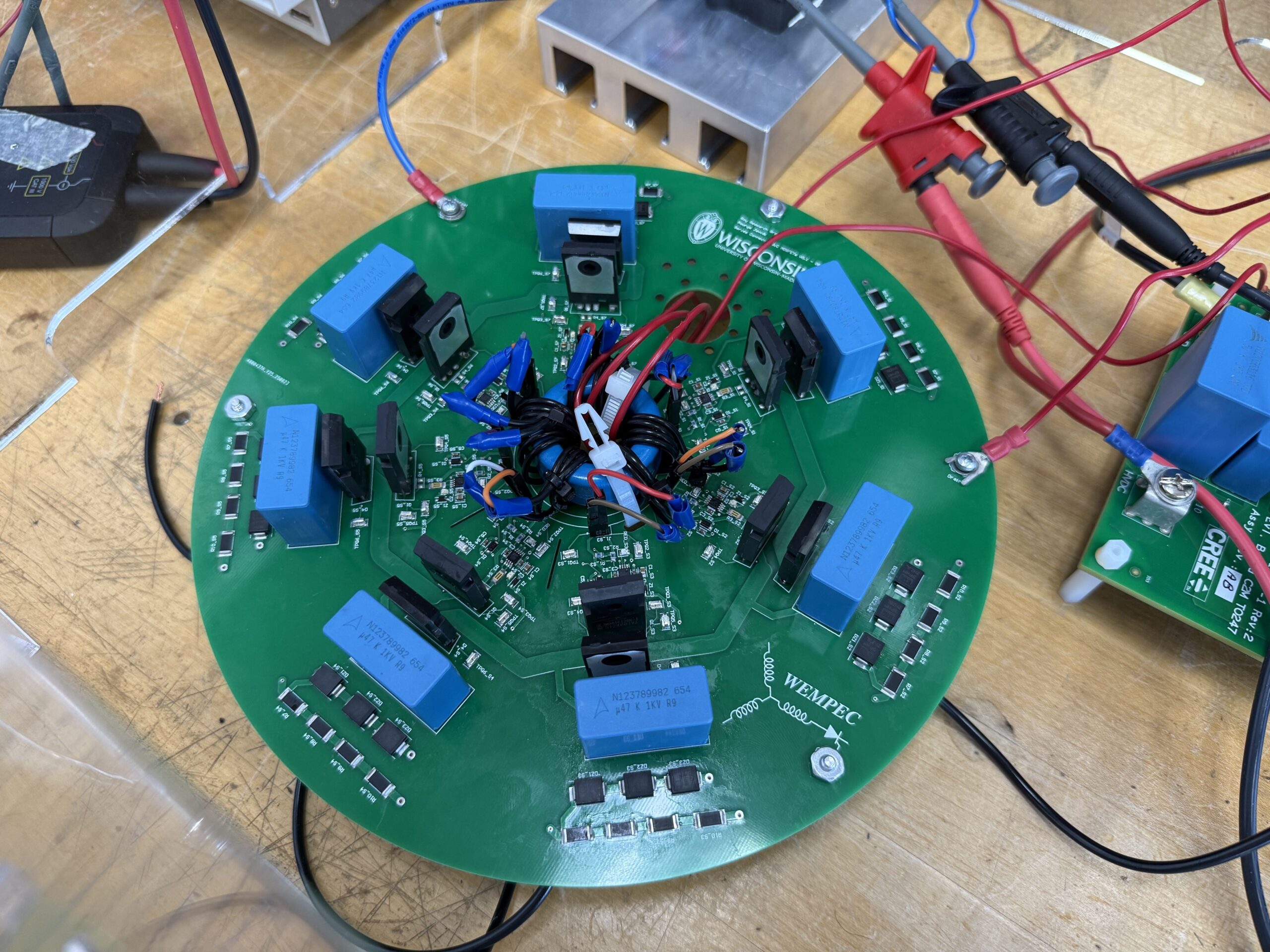
Series Connected Switch System:
Our group is working on advanced gate driver architectures and real-time control algorithms to achieve precise synchronization and robust voltage balancing across series-connected wide-bandgap devices, thereby enhancing the reliability and performance of next-generation HVPPS systems.
- Direct-switched High-Voltage Pulsed Power Supplies (HVPPS): Deliver a large DC-link voltage to the load through an Equivalent High Voltage Switch (EHVS).
- Equivalent High Voltage Switch (EHVS): Formed by series-connecting multiple SiC MOSFETs or GaN HEMTs.
- Number of devices in series: Chosen based on voltage-blocking needs, reliability margins, and derating requirements.
- Benefits of EHVS approach: Enables higher voltage and high-frequency operation beyond the capability of a single device.
- Critical technical challenges:
- First challenge: Uniform static voltage sharing must be ensured when all devices are OFF, as parasitic capacitances and non-linear device capacitances tend to cause uneven voltage distribution.
- Second challenge: Precise and synchronous switching is required during turn-on and turn-off transitions to avoid switching delays that lead to transient overvoltage stress and unbalanced dynamic voltage sharing.
- Consequences if imbalances are not properly managed: Can result in localized over-stress, device failure, and compromised system reliability.
Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) Power Systems:
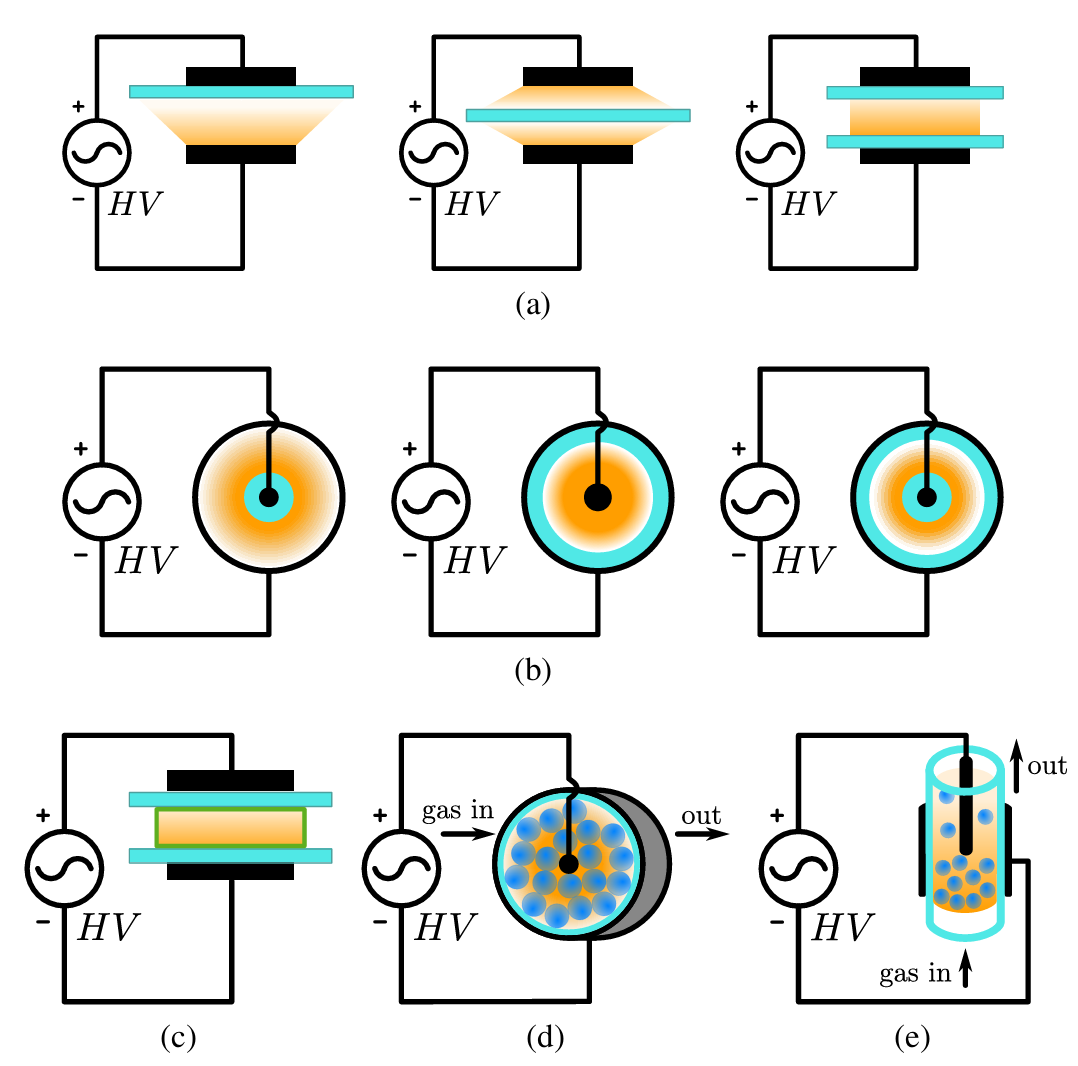
Our group researches high-voltage, high-frequency power supplies for efficient and controllable Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) plasma generation. By analyzing non-linear behavior of DBD loads and combining resonant inverters, pulsed power supplies, and advanced HV transformer design, we enable reliable excitation across diverse DBD reactor geometries.
- What is DBD?
Non-thermal plasma generated by dielectric-insulated electrodes. Operates at atmospheric pressure and supports applications ranging from food sterilization and chemical conversion to surface treatment and biomedical processing. - Sinusoidal Power Supplies:
Resonant LC/LCL and Class-E inverters provide adjustable HF sinusoidal excitation with soft-switching, high gain, and efficient integration of capacitive DBD loads. - Pulsed Power Supplies (PPS):
Marx generators, pulse-forming networks, and flyback-based pulsers enable nanosecond–microsecond pulses with sharp rise times for enhanced ionization and precise energy delivery. - Waveform & Frequency Control:
Custom waveform shaping—sinusoidal, square, unipolar/bipolar pulses—with frequencies from Hz to MHz allows optimization of plasma uniformity, discharge mode, and application-specific performance. - Reactor Geometry Support:
Designed for VDBD, SDBD, in-package DBD, packed/fluidized-bed DBD, flexible DBD, and floating-electrode configurations, each with distinct impedance and HV requirements. - Key Challenges:
Highly capacitive, threshold-triggered loads; maintaining soft-switching over varying conditions; minimizing transformer parasitics; and ensuring fast, well-shaped HV pulses without ringing.
Our efforts advance next-generation DBD systems by improving plasma stability, energy efficiency, and controllability for industrial and scientific applications.
Hybrid & Renewable Power Source Conversion
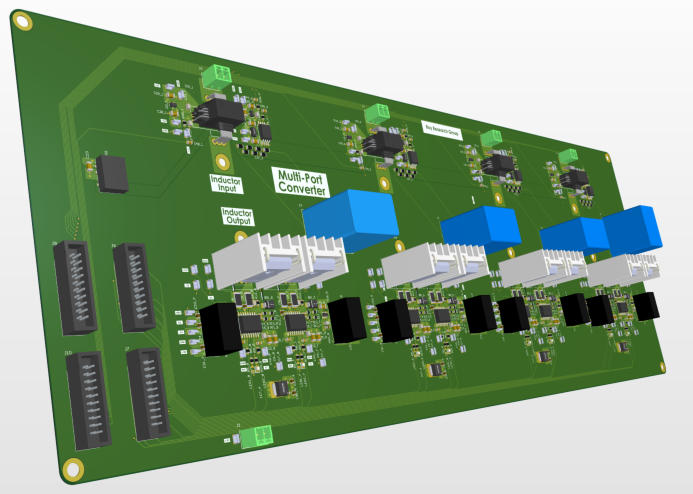
Our group develops high-gain, multi-port power converter architectures to efficiently interface renewable sources, energy storage systems, and DC loads. By extending the capabilities of the Extended-Duty-Ratio (EDR) converter, we create compact, scalable solutions for next-generation hybrid energy systems.
- Multi-Port EDR Converter:
Enables multiple input sources (e.g., PV, battery, fuel cell) to be connected to individually controlled phases, allowing independent regulation such as MPPT, battery charge/discharge control, or load management. - High Voltage Gain with Compact Design:
Interleaved inductors and switched-capacitor stages provide significantly higher voltage gain than a conventional boost converter, while distributing device stress and maintaining high efficiency. - Reduced Voltage Stress via Phase-Shift Control:
A modified phase-shift strategy minimizes switch voltage stress across wide duty-ratio ranges, enabling the use of lower-voltage, lower-loss semiconductor devices . - Bidirectional Operation:
Supports energy storage interfaces by replacing diodes with complementary active switches, enabling regulated charge/discharge and flexible power-flow control for hybrid systems. - Applications:
Renewable energy integration, hybrid DC microgrids, PV-battery systems, electrolyzers, EV charging nodes, and high-gain DC distribution.
Our work enables compact, high-efficiency power processing for modern hybrid and renewable energy systems while providing the control flexibility required for diverse source characteristics.
Space Power Management :
- Core-less magnetics & system-level optimization for deep-space reliability
- Radiation-hardened wide-bandgap (WBG) devices
- Modular + redundant architectures with interleaving
- Partial power processing → maximum efficiency, minimum mass
- Active capacitor circuits for ultra-low mass energy storage